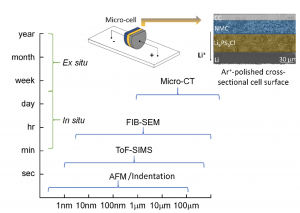
Multi-dimensional battery interfacial studies
Solid-state battery interfacial issues are critical challenges that hinder the widespread adoption of these promising energy storage devices. The interfaces between the solid electrolyte, electrode materials, and current collectors play a crucial role in determining the overall performance, stability, and lifespan of the battery. Issues such as poor interfacial adhesion, limited ion transport, and side reactions at the interfaces can lead to decreased energy efficiency, capacity fading, and even premature failure of the battery.
Our objective is to address these interfacial issues by integrating multiple cutting-edge analytical instruments for comprehensive investigations of the fundamental properties of battery interfaces. The integration of multiple analytical instruments will allow us to obtain a comprehensive and detailed picture of the interfacial behavior, providing insights into the mechanisms governing the battery’s performance and degradation. This knowledge will guide the development of strategies to improve interfacial adhesion, enhance ion transport, mitigate side reactions, and optimize the overall interface design.
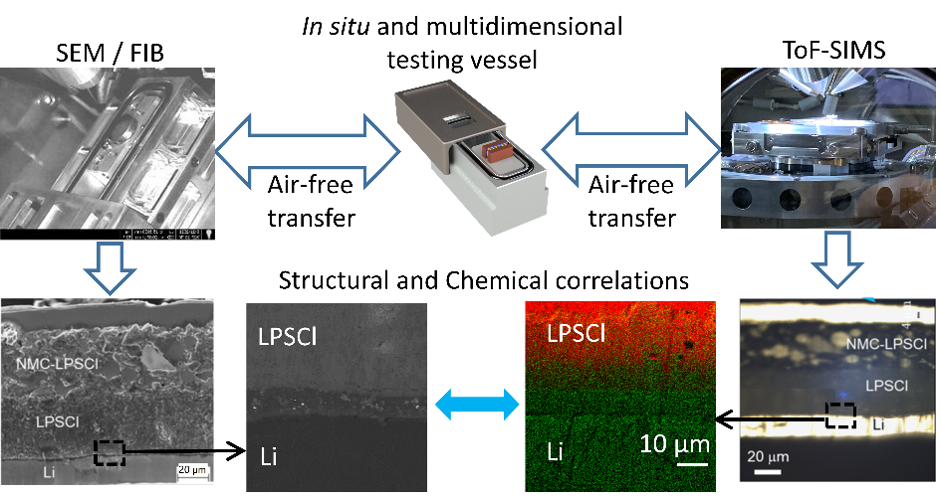
Example of the SEM — ToF-SIMS joint analysis: